Introduction
The pericardium is a double-layered, fibroelastic sac surrounding the heart, consisting of a visceral layer over the epicardium and a richly innervated parietal layer, separated by a potential space that normally holds 15 to 50 mL of serous fluid.[1][2] Pericarditis refers to inflammation of the pericardial sac surrounding the heart and is the most common pathological condition affecting the pericardium.[3] This condition can be classified into acute, incipient or subacute, chronic, and recurrent pericarditis, which is estimated to occur in about 15% to 30% of cases.[3] Pericarditis may also present alongside other pericardial syndromes, including pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, and effusive-constrictive pericarditis.[2][4][5][6][7]
Pericardial inflammation often leads to fluid accumulation within the pericardial sac, resulting in a pericardial effusion, which can be serous, hemorrhagic, or purulent, depending on the etiology. The fluid accumulation can become hemodynamically significant, especially if the effusion is large or accumulates rapidly, as the fluid may extrinsically compress the cardiac chambers, restrict diastolic filling, and lead to cardiac tamponade.[2][4] This condition can present with obstructive shock and is considered a medical emergency that requires immediate intervention.
Additionally, pericarditis may lead to pericardial thickening, which can rarely manifest as constrictive pericarditis months or even years after the initial insult. A more recently described condition known as effusive-constrictive pericarditis occurs when fluid accumulates around the heart, yet constrictive physiology, eg, respiratory-enhanced interventricular dependence, a restrictive E/A filling pattern (ratio of early [E] to late [A] diastolic velocities), and mitral annulus reversus with septal e' velocity greater than lateral e'—persists even after pericardiocentesis. This indicates the presence of constrictive pathology that is independent of the pericardial effusion.[6][8] The aforementioned pericardial syndromes may occur alongside acute pericarditis but are not required for its diagnosis.
Etiology
Register For Free And Read The Full Article
Search engine and full access to all medical articles
10 free questions in your specialty
Free CME/CE Activities
Free daily question in your email
Save favorite articles to your dashboard
Emails offering discounts
Learn more about a Subscription to StatPearls Point-of-Care
Etiology
The 2015 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines for diagnosing and managing pericardial diseases categorize the causes of acute pericarditis into 2 main groups—infectious and noninfectious.[9]
Infectious Causes of Pericarditis
Viruses are the most common infectious agents causing pericarditis, including coxsackieviruses A and B, echoviruses, adenoviruses, parvovirus B19, HIV, influenza, and several herpesviruses, eg, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV).[9][10]
New-onset pericarditis can also develop with COVID-19 infection, estimated to occur in approximately 1.5% of cases. This has been shown to portend a higher risk of significant adverse events. In one study, 6-month all-cause mortality was found to be double that of matched cohorts (15.5% versus 6.7%, P < .0001).[11]
Bacterial pericarditis occurs infrequently in developed countries; however, tuberculosis remains widespread in developing regions and is the most common cause of pericarditis in endemic areas.[12] This is particularly true for HIV-positive patients, among whom the infection rate continues to rise.[13] Less commonly, bacteria such as Coxiella burnetii, Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus can cause pericarditis, with life-threatening cases of purulent cardiac tamponade documented in the literature.[14]
In rare instances, fungal organisms such as Histoplasma, Coccidioides, Candida, and Blastomyces, as well as parasitic species like Echinococcus and Toxoplasma, can also cause pericarditis.[15] When these pathogens are identified, an underlying immunocompromised state should be strongly considered, as many fungi and parasites—particularly Histoplasma and Toxoplasma—are opportunistic infections and have been described predominantly in HIV-positive patients.
Noninfectious Causes of Pericarditis
Noninfectious causes of pericarditis are varied and include malignancy (often secondary to metastatic disease), connective tissue disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and Behçet's disease, and metabolic conditions (eg, uremia and myxedema).[7][9]
Additional Causes of Pericarditis
Trauma can also lead to pericarditis, which may present as an early onset following injury or, more commonly, as a delayed inflammatory reaction.[16] Dressler syndrome, also known as "late post-myocardial infarction syndrome," is a well-recognized post-cardiac injury syndrome characterized by pericarditis following acute coronary syndrome, with a delayed inflammatory response typically occurring several weeks after the initial event.[2][5][17] Notably, Dressler syndrome is believed to occur secondary to the formation of antimyocardial antibodies as a delayed autoimmune response, leading to pericarditis symptoms in the late postmyocardial infarction stage.[18] When first described, Dressler syndrome was estimated to occur in 5% to 7% of myocardial infarction cases; however, it has become uncommon due to advancements in the management of acute coronary syndrome, which have led to early revascularization and a reduced burden of myocardial injury. Other postcardiac injury syndromes can also arise following percutaneous intervention, cardiac surgery, or blunt trauma.[17]
Multiple medications have been implicated in drug-induced pericarditis, although its incidence remains rare. Historically, certain drugs, eg, procainamide, hydralazine, and isoniazid, have been associated with medication-induced SLE, leading to serositis and pericardial involvement manifesting as pericarditis.[19] More recently, checkpoint inhibitors, eg, ipilimumab and nivolumab, have been increasingly recognized as causes of cardiac toxicity, including myocarditis and pericarditis. The 2 most prominent classes of medications are monoclonal antibodies targeting cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), along with its ligand PD-L1. These therapies have seen numerous advancements in oncology and are likely to be implicated in more cases of cardiac toxicity as their clinical use continues to rise.[20]
In the post-COVID era, a new etiology emerged, with pericarditis occasionally being attributed to the mRNA vaccines. This appears to be rare. In one study, the incidence was 0.001%, and occurred only within 28 days of the second vaccine dose.[21] Overall, the risk is considered extremely small and may, in fact, be lower than that associated with contracting COVID-19 itself.
Miscellaneous conditions (eg, amyloidosis and sarcoidosis) should also be considered, particularly when suggestive systemic findings accompany pericarditis.[22] However, in up to 90% of cases, no clear etiology is identified, leading to a diagnosis of idiopathic acute pericarditis. This form is the most commonly encountered in clinical practice, and extensive testing is rarely necessary unless specific clinical suspicion exists.
In recurrent pericarditis, recent findings attribute recurrent symptoms to an autoinflammatory cycle, where inflammasome dysfunction leads to IL-1 (interleukin 1) overproduction.[23] The RHAPSODY trial subsequently showed great promise when rilonacept (which functions as an IL-1 binder or "decoy receptor") was utilized.[24]
Epidemiology
The yearly incidence of acute pericarditis reaches approximately 0.03% within the general population. About 10% of affected individuals may require hospitalization, while 15% to 30% may experience recurrent episodes. This condition occurs more frequently in young males and represents the most common form of inflammatory heart disease.[25]
Pathophysiology
The pericardium serves several functions, including anchoring the heart within the thoracic cavity, forming a barrier against extrinsic infections, and facilitating dynamic interaction between cardiac chambers.[2] Notably, the pericardium is not necessary for survival, as cases have been reported of congenital complete absence of the pericardium, which has been incidentally discovered in asymptomatic individuals.[26] Despite potential concerns about increased cardiac mobility and displacement within the chest cavity, studies show that these patients have comparable left ventricular ejection fractions and life expectancies to the general population.[27]
The parietal layer’s rich innervation makes it highly sensitive to inflammation caused by infectious, autoimmune, or traumatic insults, often resulting in severe retrosternal chest pain, as seen in acute pericarditis.[1] This explains why over 90% of patients with pericarditis present with chest discomfort.[3] In cases of pericardial effusion, increased pericardial compliance allows the sac to dilate over time in response to slowly accumulating fluid, preventing compression of the cardiac chambers.[2] Consequently, the rate of fluid accumulation—and the resulting pressure changes—often has a greater impact than the volume in determining the hemodynamic effects on the heart. As a result, a relatively small pericardial effusion can lead to life-threatening tamponade if it accumulates rapidly, while a gradual process, such as malignancy, may allow a large pericardial effusion to develop over weeks before causing constrictive physiology in the cardiac chambers.[28]
History and Physical
Clinical Features
Pericarditis is classified based on duration. Acute pericarditis lasts less than 4 to 6 weeks, incessant pericarditis persists beyond 4 to 6 weeks but resolves within 3 months, and chronic pericarditis extends beyond 3 months. Recurrent pericarditis refers to a new episode that occurs following a symptom-free interval of 4 to 6 weeks between episodes.[27]
Acute pericarditis accounts for approximately 5% of nonischemic chest pain presentations in emergency departments and 0.1% of inpatient admissions.[27] The classical presentation involves central, severe chest pain that is pleuritic (worsens with deep inspiration) and positional (improves with sitting up and leaning forward). The pain may radiate to the trapezius ridges if the phrenic nerve is inflamed as it passes through the pericardium.[27][29] When myocarditis is also present, the pain may be less specific, with symptoms of heart failure (eg, shortness of breath) potentially accompanying the presentation.[30]
Pericardial pain can be distinguished from ischemic pain, which typically worsens with exertion or emotional stress and improves with rest or nitroglycerin. Ischemic pain is generally nonpositional, nonpleuritic, and nonreproducible with palpation. However, atypical presentations of ischemic pain are common, making clinical differentiation challenging.[31] Pleuritic chest pain that does not improve with sitting up and is accompanied by respiratory symptoms (eg, cough or sputum production) is more likely secondary to pleurisy. In contrast, lower chest pain that improves with leaning forward, is nonpleuritic, and occurs alongside food intake should raise suspicion for abdominal conditions, eg, esophagitis or acute pancreatitis.
Certain clinical diagnostic clues may be suggestive of the underlying cause of pericarditis. Viral pericarditis is often associated with a flu-like prodrome, eg, fever or upper respiratory symptoms. Autoimmune and inflammatory etiologies may present with systemic manifestations, including polyarthritis in rheumatoid arthritis, skin and kidney manifestations in SLE, or asterixis and encephalopathy in uremia.[32][33] A history of prior pericardial injury (eg, cardiac surgery or blunt trauma) should also be considered, as symptoms may emerge days to weeks after the initial event.[34]
Physical Examination Findings
Auscultation typically reveals a left parasternal pericardial friction rub, characterized by a rasping, scratchy triphasic sound that corresponds to friction between the pericardial layers during atrial systole, ventricular systole, and early ventricular diastole. This friction rub is reported to be present in 35% to 85% of cases at some point during the illness.[35] However, eliciting the friction rub during an examination can be challenging. The physician should listen to multiple precordial locations in various positions, including the lateral decubitus position at end-expiration, using the diaphragm to enhance the likelihood of detection. Listening to precordial movements more than once is essential, as pericardial friction rubs can appear and disappear intermittently. They may be discernible only at initial presentation or can become louder and more noticeable as an existing pericardial effusion resolves, facilitating friction between the visceral and parietal layers.
When present, particularly as a triphasic sound, a pericardial friction rub is highly specific for diagnosing acute pericarditis. However, one component may sometimes be absent, resulting in a biphasic sound. This should not be confused with a pleural rub, which may produce a similar sound but is related to respiration rather than the cardiac cycle.[36] Asking the patient to hold their breath while auscultating can help differentiate between the 2 rubs. Even in the absence of a pericardial friction rub, the diagnosis of acute pericarditis should still be considered if clinical suspicion is strong, as its absence does not rule out the diagnosis.
Evaluation
The differential diagnosis for chest pain should include angina due to stable ischemic heart disease or acute coronary syndrome, subendocardial ischemia associated with aortic stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, aortic dissection, myocarditis, pleurisy secondary to pulmonary embolism or pneumonia, costochondritis, esophageal spasm, peptic ulcer disease, or referred pain from another organ (eg, acute cholecystitis). In the acute setting, excluding life-threatening etiologies is critical before considering the diagnosis of acute pericarditis, especially in cases of uncertainty.[37]
All patients with suspected acute pericarditis should undergo an ECG, echocardiogram, and chest x-ray. Myocardial inflammatory and injury markers, as well as troponins, should also be measured (Class I, LOE C).[32][38][39] In regions where tuberculosis is not a concern, the initial workup is often sufficient, as most cases respond promptly to empiric treatment.[38] However, additional testing may be warranted if a specific cause is suspected and should be tailored to the suspected etiology.
Electrocardiograph Assessment
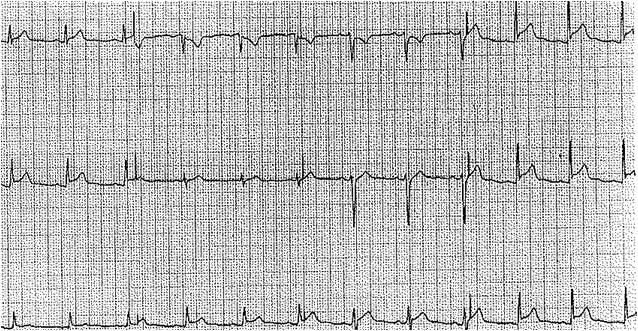
More than half of patients with acute pericarditis exhibit characteristic electrocardiogram (ECG) changes that evolve through 4 stages over several weeks, showing significant temporal variability (see Image. Electrocardiographic Findings in Acute Pericarditis), including:
- Stage I typically presents with diffuse, concave ST-segment elevation, accompanied by reciprocal ST depression in the lead AVR. This stage may also feature PR segment elevation in lead AVR (and possibly V1), which can effectively differentiate acute pericarditis from myocardial infarction.[34] Although localized pericarditis can present with ST elevations in specific leads, diffuse ECG changes are more commonly observed.
- Stage II typically occurs within the first week and shows normalization of ST and PR segment changes.
- Stage III is characterized by widespread T-wave inversions.
- Stage IV involves the eventual normalization of T waves.[40]
The initial ST elevation in pericarditis should not be confused with an acute injury pattern, where ST elevation appears in a localized distribution and is concave down, unlike the concave-up pattern seen in pericarditis. Acute injury patterns are also typically associated with reciprocal ST depressions in multiple leads (not limited to AVR, as in pericarditis), and Q waves often emerge in the same distribution—or develop shortly thereafter—as part of the natural progression of acute or subacute myocardial infarction.
The differential diagnosis for ST elevations should include early repolarization abnormalities, which are commonly observed in healthy individuals. These abnormalities are characterized by an elevated J-point, often presenting as an initial slur at the beginning of the ST segment. While they may appear in several leads, they are typically not diffuse.[41]
Clinically, acute pericarditis is indicated by a characteristic description of chest pain and the presence of a pericardial friction rub upon auscultation. However, laboratory studies, ECG, and echocardiography are often necessary to confirm the diagnosis. According to the 2015 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines, a diagnosis of acute pericarditis requires the presence of at least 2 out of 4 following criteria:
- Pericardial chest pain
- Pericardial rubs
- New widespread ST elevation or PR depression on ECG
- New or worsening pericardial effusion.
Laboratory Studies
Initial evaluation studies, including a complete blood count, basic metabolic panel, liver function tests, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels, are recommended if further evaluation is pursued, as they may suggest specific etiologies (eg, uremia or infection). Blood cultures, viral seromarkers, and tuberculosis testing, eg, purified protein derivative (PPD) or interferon-γ release assays (IGRAs), may also be indicated in select patients. HIV testing, using antibody/antigen tests or nucleic acid testing, should be performed if an opportunistic infection is identified, given the strong correlation between immunocompromised states and fungal or tuberculosis infections.[38] Additional workups may include testing for antinuclear antibodies or conducting targeted investigations for suspected systemic diseases (eg, sarcoidosis).
Supporting findings may include elevated inflammatory biomarkers (eg, erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR], C-reactive protein [CRP], and leukocytosis) and evidence of pericardial inflammation on advanced imaging, such as cardiac computed tomography (CT) and cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). While pericardial effusion is often present, this clinical feature is not required for a definitive diagnosis of acute pericarditis.[34]
Pericardial fluid analysis with cytology is recommended to confirm malignant pericardial disease (Class I, LOE B). Additional testing may include pericardial biopsy and tumor marker assessments, such as carcinoembryonic antigen and CA-19 (Class IIa, LOE B). However, evidence supporting their accuracy in distinguishing between malignant and nonmalignant effusions is limited.[42] If a definitive diagnosis of viral pericarditis is sought, a comprehensive histological, cytological, and molecular analysis should be performed on the obtained pericardial fluid and any pericardial biopsy. It should be noted that routine viral serological testing is not recommended, except for HIV and hepatitis C (HCV).[43]
Imaging Studies
The 2015 ESC guidelines recommend CT or MRI as Class I options for second-line testing.[38][44] Cardiac CT may reveal thickened pericardial layers and pericardial fluid accumulation, with calcification often prominent in cases of constrictive pericarditis. However, cardiac CT is not suitable for assessing hemodynamic compromise in cardiac tamponade, and echocardiography is more effective for this purpose. Additionally, cardiac CT carries an increased risk of radiation exposure. Cardiac MRI provides detailed information, including late gadolinium enhancement within the pericardial layers or myocardium in cases of myopericarditis. This imaging technique can also detect intramyocardial strands associated with fibrinous pericardial effusion and is highly effective for evaluating myocardial function and identifying suspicious pericardial masses.[45]
Diagnostic Pericardiocentesis
Emergent pericardiocentesis is recommended for patients presenting with cardiac tamponade.[46] Pericardiocentesis may also be performed electively in cases of moderate-to-large pericardial effusion without immediate hemodynamic compromise, with a chest tube left in place for several days or until drainage ceases. Diagnostic pericardiocentesis is also indicated when an infectious cause of acute pericarditis is suspected, even with a small effusion. Bacterial, fungal, and tuberculosis studies on pericardial fluid should include basic chemistry, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and fluid cultures. Blood cultures should also be obtained when appropriate.[46] Purulent effusions, although rare, are associated with high mortality and should be treated aggressively. Urgent drainage is necessary, followed by intra-pericardial thrombolysis in cases of loculated effusions (Class IIa, LOE C). The aspirate may appear overtly purulent, and a low pericardial-to-serum glucose ratio of less than 0.3, along with neutrophilic predominance (mean cell count of 2.8/μL, with 92% neutrophils), helps differentiate it from mycobacterial or neoplastic pericarditis.[43]
An exudative pericardial effusion warrants empiric anti-tuberculosis treatment in regions where tuberculosis is endemic, even while cultures are pending. If a positive diagnosis of tuberculosis is confirmed, medical therapy for at least 6 months is recommended (Class I, LOE C). Pericardiectomy should be considered if no improvement in symptoms is noted after 4 to 8 weeks of therapy (Class I, LOE C).[47] Pericardial thickening is present in most cases of tuberculosis pericarditis. Before effective medical treatment was available, effusive pericarditis would progress to constrictive pericarditis in up to half of all cases. Studies have shown that the addition of high-dose adjunctive prednisolone can reduce the incidence of constrictive pericarditis, but it may also increase the risk of HIV-associated malignancies.[48] Consequently, adjunctive steroids may be considered in HIV-negative patients but should be avoided in HIV-positive patients, as per ESC guidelines (Class IIb, LOE C).[43]
Pericardial fluid analysis with cytology is recommended to confirm malignant pericardial disease (Class I, LOE B). Additional testing may include pericardial biopsy and tumor marker assessments, eg, carcinoembryonic antigen and CA-19 (Class IIa, LOE B). However, evidence supporting their accuracy in distinguishing between malignant and nonmalignant effusions is limited.[42] If a definitive diagnosis of viral pericarditis is sought, a comprehensive histological, cytological, and molecular analysis should be performed on the obtained pericardial fluid and any pericardial biopsy. It should be noted that routine viral serological testing is not recommended, except for HIV and hepatitis C (HCV).[43]
The incidence of uremic pericarditis has significantly declined with the introduction of dialysis.[49] In this subpopulation, pleuritic chest pain is less prevalent, and ECG changes are often absent. In chronic cases, these patients are also more likely to develop pericardial effusions, but often without progression to acute cardiac tamponade. If pericardiocentesis is performed, the aspirate is often bloody.[50]
Additional Diagnostic Studies
Cardiac catheterization may be considered to assess for diastolic pressure equalization and respiratory interventricular dependence if constrictive pericarditis is suspected. However, cardiac catheterization is not recommended solely for diagnosing acute pericarditis.[50]
Treatment / Management
Acute Pericarditis Management
Treatment for acute pericarditis begins with addressing the underlying cause. Patients with uremic pericarditis should receive more frequent dialysis, while those with malignancy or tuberculosis require therapy targeted at the primary disease. For tuberculosis, the standard treatment involves a quadruple antibiotic regimen (rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol) for at least 2 months, followed by isoniazid and rifampicin for a total of 6 months. This may be combined with adjunctive high-dose prednisolone, as previously discussed.[47](A1)
Most patients will have idiopathic acute pericarditis, which can be safely managed on an outpatient basis with medical therapy alone. Activity restrictions beyond a sedentary lifestyle are advised until symptoms resolve or cardiac enzyme levels normalize.[51] Patients exhibiting markers of poor prognosis or those who do not respond to therapy within 1 week should be admitted for further evaluation. These markers include fever (>38 °C), a subacute or recurrent presentation, the presence of a large pericardial effusion (>20 mm in thickness), or echocardiographic signs of cardiac tamponade physiology (eg, right ventricular diastolic collapse, a transmitral flow respirophasic variation of more than 25% throughout the respiratory cycle, and a dilated inferior vena cava with inspiratory collapse of less than 50%, indicating elevated right atrial filling pressures).[51][52] Minor risk markers include immunosuppression, trauma, or myopericarditis, where patients exhibit troponin elevation alongside elevated inflammatory markers.
Pharmacologic Management
In most patients, empiric treatment with high-dose anti-inflammatory agents, in addition to colchicine, is recommended. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) therapy should continue until symptom relief is achieved, which typically occurs within 3 days to 2 weeks. Possible regimens include ibuprofen 600 mg every 8 hours, indomethacin 25 to 50 mg every 8 hours, or naproxen 500 to 1000 mg every 12 hours.[53] Aspirin 500 to 1000 mg every 6 to 8 hours should be used instead of other NSAIDs in patients postmyocardial infarction or those already on antiplatelet therapy (Class I, LOE C). Aspirin is also considered first-line therapy during the first trimester of pregnancy, but is contraindicated after 20 weeks of gestation, where paracetamol may be used instead.
The COPE trial randomized 120 patients to receive either conventional therapy with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA, also known as aspirin) or conventional therapy with adjunctive colchicine, following them for 18 months. The colchicine group showed less symptom persistence at 72 hours (11.7% versus 36.7%; P = .003) and significantly fewer recurrent episodes (10.7% versus 32.3%; P = .004) compared to the control group.[54] Several studies have demonstrated that colchicine effectively reduces the recurrence of pericarditis, with further episodes decreased by approximately half.[55] Consequently, adjunctive colchicine therapy is now recommended for most patients with acute pericarditis for a duration of 3 to 6 months. The recommended dosage is 0.6 mg orally twice daily for patients with a body weight of more than 70 kg and 0.5 mg orally once daily for those with a body weight of <70 kg. Colchicine is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (Class III, LOE C).(A1)
Low-to-moderate doses of prednisone (0.2–0.5 mg/kg/d or equivalent) with a slow taper may be considered if NSAIDs or ASA and colchicine are contraindicated. While the latter can often provide rapid clinical improvement, ample evidence suggests that their use increases the risk of recurrent pericarditis after therapy is discontinued.[56] Consequently, corticosteroids are not recommended as first-line therapy for most patients unless an autoimmune etiology for acute pericarditis is identified. The initial dose should be maintained until symptom relief and normalization of the CRP level are achieved, after which it should be tapered down slowly.[56](A1)
Response to therapy is assessed clinically based on symptom relief, although serial CRP measurements can also be helpful. If an incomplete response to anti-inflammatory agents (ASA or NSAIDs) with adjunctive colchicine is noted, the addition of steroids as part of a triple therapy regimen should be considered after excluding an infectious etiology.[57](B2)
Certain forms of acute pericarditis, eg, iatrogenic and uremic pericarditis, have been associated with an increased risk of hemorrhagic pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade, according to small studies. Therefore, while strong evidence is lacking, stopping anticoagulation when feasible in these patients may be prudent.[50] However, no formal guidelines exist, and recommendations are based solely on expert opinion. Additionally, concomitant use of ASA should be avoided unless a strong indication is present, eg, recent stent placement or postacute coronary syndrome.(B3)
Recurrent Pericarditis Management
For patients who develop a first recurrence (ie, return of pericarditis symptoms, after a 4 to 6 week interval of being symptom-free), restarting patients on NSAID therapy and colchicine is recommended, though the latter should be prolonged for 6 to 12 months. If that fails, then low-dose steroids with a slow taper can be considered.
For corticosteroid-dependent recurrent pericarditis, steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), or anakinra (an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist) are considered reasonable options.[58] In late findings, results from the RHAPSODY phase 3 trial have introduced rilonacept, which functions as an IL-1 receptor antagonist by binding IL-1 particles, as a viable option for recurrent pericarditis. Patients receiving rilonacept reported significant clinical improvement within 12 weeks of treatment and a lower risk of recurrence (hazard ratio: 0.04, CI: 0.01-0.18) compared to those receiving placebo. The latter group also showed statistically significant clinical improvement after eventually receiving bailout therapy. Still, more real-world data would be needed to cement new practice recommendations, but early data is promising.(B2)
If all medical therapy fails, pericardiectomy remains an option of last resort and is rarely performed.[59](B2)
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnoses that should also be considered when evaluating pericarditis include:
- Pleurisy
- Pneumonia
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Bony pain
- Costochondritis
- Angina
Prognosis
The overall prognosis for acute pericarditis is excellent, with most patients experiencing complete recovery.
Complications
Up to 30% of patients who are not treated with colchicine may experience recurrent pericarditis. Constrictive pericarditis is exceedingly rare following idiopathic acute pericarditis, occurring in <1% of cases. However, the risk of constrictive pericarditis increases with specific etiologies, particularly purulent bacterial or tuberculosis pericarditis, where the incidence of constrictive pericarditis may rise to as high as 30%.[60][61] Cardiac tamponade, the most feared acute complication, rarely occurs after idiopathic pericarditis but is more commonly associated with malignancy and infectious causes of pericarditis.[62]
Deterrence and Patient Education
While episodes of acute pericarditis cannot be prevented, adherence to prescribed therapy (eg, completing a full course of colchicine for 3 to 6 months and avoiding heavy exertion in the early phase) can significantly lower the chance of a recurrent episode.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Effective diagnosis and management of pericarditis demand a coordinated, interprofessional approach involving cardiologists, radiologists, cardiac surgeons, infectious disease specialists, primary care providers, nurse practitioners, and other key health professionals. Due to the condition’s variable and often vague presentation—frequently mimicking myocardial infarction, pleurisy, or angina—prompt cardiology consultation is critical before initiating therapy. Physicians and advanced practitioners must recognize subtle clinical cues and utilize diagnostic tools such as ECG and echocardiography to confirm pericarditis and rule out complications like tamponade. Early identification of pericardial effusion allows for timely decision-making regarding conservative treatment versus procedural intervention, such as pericardiocentesis, which necessitates proper patient preparation and education by nurses and support staff.
Ongoing management relies on collaborative care. Nurses play a vital role in monitoring patients for symptom progression and complications, especially in those with uremic pericarditis, who are at high risk for recurrence. Pharmacists ensure patients understand the rationale behind NSAID and colchicine use, reinforce adherence, and educate on potential side effects. Clear, consistent communication among team members enhances patient-centered care and safety by preventing delays, reducing readmissions, and ensuring follow-up. Recovery often spans weeks to months, and multidisciplinary coordination remains crucial for supporting the patient through the entire continuum of care, promoting optimal outcomes and functional recovery.
Media
(Click Image to Enlarge)
References
Hoit BD. Anatomy and Physiology of the Pericardium. Cardiology clinics. 2017 Nov:35(4):481-490. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2017.07.002. Epub [PubMed PMID: 29025540]
Little WC, Freeman GL. Pericardial disease. Circulation. 2006 Mar 28:113(12):1622-32 [PubMed PMID: 16567581]
Imazio M, Gaita F, LeWinter M. Evaluation and Treatment of Pericarditis: A Systematic Review. JAMA. 2015 Oct 13:314(14):1498-506. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.12763. Epub [PubMed PMID: 26461998]
Level 1 (high-level) evidenceSpodick DH. Acute cardiac tamponade. The New England journal of medicine. 2003 Aug 14:349(7):684-90 [PubMed PMID: 12917306]
Imazio M, Lazaros G, Brucato A, Gaita F. Recurrent pericarditis: new and emerging therapeutic options. Nature reviews. Cardiology. 2016 Feb:13(2):99-105. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.115. Epub 2015 Aug 11 [PubMed PMID: 26259934]
Maisch B. [Management of pericarditis and pericardial effusion, constrictive and effusive-constrictive pericarditis]. Herz. 2018 Nov:43(7):663-678. doi: 10.1007/s00059-018-4744-9. Epub [PubMed PMID: 30315402]
Khandaker MH, Espinosa RE, Nishimura RA, Sinak LJ, Hayes SN, Melduni RM, Oh JK. Pericardial disease: diagnosis and management. Mayo Clinic proceedings. 2010 Jun:85(6):572-93. doi: 10.4065/mcp.2010.0046. Epub [PubMed PMID: 20511488]
Oh JK, Hatle LK, Seward JB, Danielson GK, Schaff HV, Reeder GS, Tajik AJ. Diagnostic role of Doppler echocardiography in constrictive pericarditis. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 1994 Jan:23(1):154-62 [PubMed PMID: 8277074]
Adler Y, Charron P. The 2015 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases. European heart journal. 2015 Nov 7:36(42):2873-4. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv479. Epub [PubMed PMID: 26547486]
Imazio M, Brucato A, Derosa FG, Lestuzzi C, Bombana E, Scipione F, Leuzzi S, Cecchi E, Trinchero R, Adler Y. Aetiological diagnosis in acute and recurrent pericarditis: when and how. Journal of cardiovascular medicine (Hagerstown, Md.). 2009 Mar:10(3):217-30. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0b013e328322f9b1. Epub [PubMed PMID: 19262208]
Buckley BJR, Harrison SL, Fazio-Eynullayeva E, Underhill P, Lane DA, Lip GYH. Prevalence and clinical outcomes of myocarditis and pericarditis in 718,365 COVID-19 patients. European journal of clinical investigation. 2021 Nov:51(11):e13679. doi: 10.1111/eci.13679. Epub 2021 Sep 18 [PubMed PMID: 34516657]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceMayosi BM, Burgess LJ, Doubell AF. Tuberculous pericarditis. Circulation. 2005 Dec 6:112(23):3608-16 [PubMed PMID: 16330703]
Ntsekhe M, Mayosi BM. Tuberculous pericarditis with and without HIV. Heart failure reviews. 2013 May:18(3):367-73. doi: 10.1007/s10741-012-9310-6. Epub [PubMed PMID: 22427006]
Petcu CP, Dilof R, Bătăiosu C, Petcu PD. Purulent pericardial effusions with pericardial tamponade - diagnosis and treatment issues. Current health sciences journal. 2013 Jan:39(1):53-6 [PubMed PMID: 24778855]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceOladele RO, Ayanlowo OO, Richardson MD, Denning DW. Histoplasmosis in Africa: An emerging or a neglected disease? PLoS neglected tropical diseases. 2018 Jan:12(1):e0006046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006046. Epub 2018 Jan 18 [PubMed PMID: 29346384]
Imazio M, Negro A, Belli R, Beqaraj F, Forno D, Giammaria M, Trinchero R, Adler Y, Spodick D. Frequency and prognostic significance of pericarditis following acute myocardial infarction treated by primary percutaneous coronary intervention. The American journal of cardiology. 2009 Jun 1:103(11):1525-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.01.366. Epub 2009 Apr 8 [PubMed PMID: 19463510]
Jaworska-Wilczynska M, Abramczuk E, Hryniewiecki T. Postcardiac injury syndrome. Medical science monitor : international medical journal of experimental and clinical research. 2011 Nov:17(11):CQ13-14 [PubMed PMID: 22037738]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceWessman DE, Stafford CM. The postcardiac injury syndrome: case report and review of the literature. Southern medical journal. 2006 Mar:99(3):309-14 [PubMed PMID: 16553111]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceKatz U, Zandman-Goddard G. Drug-induced lupus: an update. Autoimmunity reviews. 2010 Nov:10(1):46-50. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Jul 23 [PubMed PMID: 20656071]
Altan M, Toki MI, Gettinger SN, Carvajal-Hausdorf DE, Zugazagoitia J, Sinard JH, Herbst RS, Rimm DL. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Pericarditis. Journal of thoracic oncology : official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. 2019 Jun:14(6):1102-1108. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.02.026. Epub 2019 Mar 7 [PubMed PMID: 30851443]
Patone M, Mei XW, Handunnetthi L, Dixon S, Zaccardi F, Shankar-Hari M, Watkinson P, Khunti K, Harnden A, Coupland CAC, Channon KM, Mills NL, Sheikh A, Hippisley-Cox J. Risks of myocarditis, pericarditis, and cardiac arrhythmias associated with COVID-19 vaccination or SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature medicine. 2022 Feb:28(2):410-422. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01630-0. Epub 2021 Dec 14 [PubMed PMID: 34907393]
Wyplosz B, Marijon E, Dougados J, Pouchot J. Sarcoidosis: an unusual cause of acute pericarditis. Acta cardiologica. 2010 Feb:65(1):83-4 [PubMed PMID: 20306895]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceBizzi E, Trotta L, Pancrazi M, Nivuori M, Giosia V, Matteucci L, Montori D, Brucato A. Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Pericarditis: Definitions and New Treatments. Current cardiology reports. 2021 Jul 28:23(9):128. doi: 10.1007/s11886-021-01549-5. Epub 2021 Jul 28 [PubMed PMID: 34319478]
Presti SL, Elajami TK, Reyaldeen R, Anthony C, Klein AL. The Role of Rilonacept in Recurrent Pericarditis. Heart international. 2021:15(1):20-25. doi: 10.17925/HI.2021.15.1.20. Epub 2021 Jul 16 [PubMed PMID: 36277322]
Lazarou E, Tsioufis P, Vlachopoulos C, Tsioufis C, Lazaros G. Acute Pericarditis: Update. Current cardiology reports. 2022 Aug:24(8):905-913. doi: 10.1007/s11886-022-01710-8. Epub 2022 May 20 [PubMed PMID: 35595949]
Kim HJ, Cho YS, Cho GY, Choi SI. Congenital absence of the pericardium. Journal of cardiovascular ultrasound. 2014 Mar:22(1):36-9. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2014.22.1.36. Epub 2014 Mar 31 [PubMed PMID: 24753808]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceShah AB, Kronzon I. Congenital defects of the pericardium: a review. European heart journal. Cardiovascular Imaging. 2015 Aug:16(8):821-7. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jev119. Epub 2015 May 23 [PubMed PMID: 26003149]
Ben-Horin S, Bank I, Guetta V, Livneh A. Large symptomatic pericardial effusion as the presentation of unrecognized cancer: a study in 173 consecutive patients undergoing pericardiocentesis. Medicine. 2006 Jan:85(1):49-53. doi: 10.1097/01.md.0000199556.69588.8e. Epub [PubMed PMID: 16523053]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceLeWinter MM. Clinical practice. Acute pericarditis. The New England journal of medicine. 2014 Dec 18:371(25):2410-6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1404070. Epub [PubMed PMID: 25517707]
Imazio M, Trinchero R. Myopericarditis: Etiology, management, and prognosis. International journal of cardiology. 2008 Jun 23:127(1):17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.10.053. Epub 2008 Jan 24 [PubMed PMID: 18221804]
Goodacre S, Locker T, Morris F, Campbell S. How useful are clinical features in the diagnosis of acute, undifferentiated chest pain? Academic emergency medicine : official journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine. 2002 Mar:9(3):203-8 [PubMed PMID: 11874776]
Buppajamrntham T, Palavutitotai N, Katchamart W. Clinical manifestation, diagnosis, management, and treatment outcome of pericarditis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand =, Chotmaihet thangphaet... 2014 Dec:97(12):1234-40 [PubMed PMID: 25764628]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceBentata Y, Hamdi F, Chemlal A, Haddiya I, Ismaili N, El Ouafi N. Uremic pericarditis in patients with End Stage Renal Disease: Prevalence, symptoms and outcome in 2017. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2018 Mar:36(3):464-466. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2017.11.048. Epub 2017 Nov 21 [PubMed PMID: 29248269]
Rossello X, Wiegerinck RF, Alguersuari J, Bardají A, Worner F, Sutil M, Ferrero A, Cinca J. New electrocardiographic criteria to differentiate acute pericarditis and myocardial infarction. The American journal of medicine. 2014 Mar:127(3):233-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 25 [PubMed PMID: 24287008]
Zayas R, Anguita M, Torres F, Giménez D, Bergillos F, Ruiz M, Ciudad M, Gallardo A, Vallés F. Incidence of specific etiology and role of methods for specific etiologic diagnosis of primary acute pericarditis. The American journal of cardiology. 1995 Feb 15:75(5):378-82 [PubMed PMID: 7856532]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceSarkar M, Madabhavi I, Niranjan N, Dogra M. Auscultation of the respiratory system. Annals of thoracic medicine. 2015 Jul-Sep:10(3):158-68. doi: 10.4103/1817-1737.160831. Epub [PubMed PMID: 26229557]
Launbjerg J, Fruergaard P, Hesse B, Jørgensen F, Elsborg L, Petri A. Long-term risk of death, cardiac events and recurrent chest pain in patients with acute chest pain of different origin. Cardiology. 1996 Jan-Feb:87(1):60-6 [PubMed PMID: 8631047]
Imazio M, Spodick DH, Brucato A, Trinchero R, Adler Y. Controversial issues in the management of pericardial diseases. Circulation. 2010 Feb 23:121(7):916-28. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.844753. Epub [PubMed PMID: 20177006]
Klein AL, Abbara S, Agler DA, Appleton CP, Asher CR, Hoit B, Hung J, Garcia MJ, Kronzon I, Oh JK, Rodriguez ER, Schaff HV, Schoenhagen P, Tan CD, White RD. American Society of Echocardiography clinical recommendations for multimodality cardiovascular imaging of patients with pericardial disease: endorsed by the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance and Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography : official publication of the American Society of Echocardiography. 2013 Sep:26(9):965-1012.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2013.06.023. Epub [PubMed PMID: 23998693]
Imazio M, Gaita F. Diagnosis and treatment of pericarditis. Heart (British Cardiac Society). 2015 Jul:101(14):1159-68. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2014-306362. Epub 2015 Apr 8 [PubMed PMID: 25855795]
Spodick DH. Differential characteristics of the electrocardiogram in early repolarization and acute pericarditis. The New England journal of medicine. 1976 Sep 2:295(10):523-6 [PubMed PMID: 950958]
Karatolios K, Pankuweit S, Maisch B. Diagnostic value of biochemical biomarkers in malignant and non-malignant pericardial effusion. Heart failure reviews. 2013 May:18(3):337-44. doi: 10.1007/s10741-012-9327-x. Epub [PubMed PMID: 22638889]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceBen-Horin S, Bank I, Shinfeld A, Kachel E, Guetta V, Livneh A. Diagnostic value of the biochemical composition of pericardial effusions in patients undergoing pericardiocentesis. The American journal of cardiology. 2007 May 1:99(9):1294-7 [PubMed PMID: 17478160]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceCosyns B, Plein S, Nihoyanopoulos P, Smiseth O, Achenbach S, Andrade MJ, Pepi M, Ristic A, Imazio M, Paelinck B, Lancellotti P, European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI), European Society of Cardiology Working Group (ESC WG) on Myocardial and Pericardial diseases. European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) position paper: Multimodality imaging in pericardial disease. European heart journal. Cardiovascular Imaging. 2015 Jan:16(1):12-31. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeu128. Epub 2014 Sep 23 [PubMed PMID: 25248336]
Bogaert J, Francone M. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in pericardial diseases. Journal of cardiovascular magnetic resonance : official journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. 2009 May 4:11(1):14. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-11-14. Epub 2009 May 4 [PubMed PMID: 19413898]
Maisch B, Seferović PM, Ristić AD, Erbel R, Rienmüller R, Adler Y, Tomkowski WZ, Thiene G, Yacoub MH, Grupo de Trabajo para el Diagnóstico y Tratamiento de las Enfermedades del Pericardio de la Sociedad Europea de Cardiología. [Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases. Executive summary]. Revista espanola de cardiologia. 2004 Nov:57(11):1090-114 [PubMed PMID: 15544758]
Level 1 (high-level) evidenceMayosi BM, Ntsekhe M, Volmink JA, Commerford PJ. Interventions for treating tuberculous pericarditis. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2002:(4):CD000526 [PubMed PMID: 12519546]
Level 1 (high-level) evidenceMayosi BM, Ntsekhe M, Bosch J, Pandie S, Jung H, Gumedze F, Pogue J, Thabane L, Smieja M, Francis V, Joldersma L, Thomas KM, Thomas B, Awotedu AA, Magula NP, Naidoo DP, Damasceno A, Chitsa Banda A, Brown B, Manga P, Kirenga B, Mondo C, Mntla P, Tsitsi JM, Peters F, Essop MR, Russell JB, Hakim J, Matenga J, Barasa AF, Sani MU, Olunuga T, Ogah O, Ansa V, Aje A, Danbauchi S, Ojji D, Yusuf S, IMPI Trial Investigators. Prednisolone and Mycobacterium indicus pranii in tuberculous pericarditis. The New England journal of medicine. 2014 Sep 18:371(12):1121-30. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1407380. Epub 2014 Sep 1 [PubMed PMID: 25178809]
Level 1 (high-level) evidenceAlpert MA, Ravenscraft MD. Pericardial involvement in end-stage renal disease. The American journal of the medical sciences. 2003 Apr:325(4):228-36 [PubMed PMID: 12695728]
Wood JE, Mahnensmith RL. Pericarditis associated with renal failure: evolution and management. Seminars in dialysis. 2001 Jan-Feb:14(1):61-6 [PubMed PMID: 11208042]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceSeidenberg PH, Haynes J. Pericarditis: diagnosis, management, and return to play. Current sports medicine reports. 2006 Apr:5(2):74-9 [PubMed PMID: 16529677]
Imazio M, Cecchi E, Demichelis B, Ierna S, Demarie D, Ghisio A, Pomari F, Coda L, Belli R, Trinchero R. Indicators of poor prognosis of acute pericarditis. Circulation. 2007 May 29:115(21):2739-44 [PubMed PMID: 17502574]
Imazio M, Brucato A, Trinchero R, Spodick D, Adler Y. Individualized therapy for pericarditis. Expert review of cardiovascular therapy. 2009 Aug:7(8):965-75. doi: 10.1586/erc.09.82. Epub [PubMed PMID: 19673674]
Imazio M, Bobbio M, Cecchi E, Demarie D, Demichelis B, Pomari F, Moratti M, Gaschino G, Giammaria M, Ghisio A, Belli R, Trinchero R. Colchicine in addition to conventional therapy for acute pericarditis: results of the COlchicine for acute PEricarditis (COPE) trial. Circulation. 2005 Sep 27:112(13):2012-6 [PubMed PMID: 16186437]
Level 1 (high-level) evidenceImazio M, Bobbio M, Cecchi E, Demarie D, Pomari F, Moratti M, Ghisio A, Belli R, Trinchero R. Colchicine as first-choice therapy for recurrent pericarditis: results of the CORE (COlchicine for REcurrent pericarditis) trial. Archives of internal medicine. 2005 Sep 26:165(17):1987-91 [PubMed PMID: 16186468]
Level 1 (high-level) evidenceLotrionte M, Biondi-Zoccai G, Imazio M, Castagno D, Moretti C, Abbate A, Agostoni P, Brucato AL, Di Pasquale P, Raatikka M, Sangiorgi G, Laudito A, Sheiban I, Gaita F. International collaborative systematic review of controlled clinical trials on pharmacologic treatments for acute pericarditis and its recurrences. American heart journal. 2010 Oct:160(4):662-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2010.06.015. Epub [PubMed PMID: 20934560]
Level 1 (high-level) evidenceImazio M, Brucato A, Cumetti D, Brambilla G, Demichelis B, Ferro S, Maestroni S, Cecchi E, Belli R, Palmieri G, Trinchero R. Corticosteroids for recurrent pericarditis: high versus low doses: a nonrandomized observation. Circulation. 2008 Aug 5:118(6):667-71. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.761064. Epub 2008 Jul 21 [PubMed PMID: 18645054]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceFinetti M, Insalaco A, Cantarini L, Meini A, Breda L, Alessio M, D'Alessandro M, Picco P, Martini A, Gattorno M. Long-term efficacy of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) in corticosteroid-dependent and colchicine-resistant recurrent pericarditis. The Journal of pediatrics. 2014 Jun:164(6):1425-31.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.01.065. Epub 2014 Mar 12 [PubMed PMID: 24630353]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceKhandaker MH, Schaff HV, Greason KL, Anavekar NS, Espinosa RE, Hayes SN, Nishimura RA, Oh JK. Pericardiectomy vs medical management in patients with relapsing pericarditis. Mayo Clinic proceedings. 2012 Nov:87(11):1062-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.05.024. Epub [PubMed PMID: 23127733]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceImazio M, Brucato A, Maestroni S, Cumetti D, Belli R, Trinchero R, Adler Y. Risk of constrictive pericarditis after acute pericarditis. Circulation. 2011 Sep 13:124(11):1270-5. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.018580. Epub 2011 Aug 15 [PubMed PMID: 21844077]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceSoler-Soler J, Sagristà-Sauleda J, Permanyer-Miralda G. Relapsing pericarditis. Heart (British Cardiac Society). 2004 Nov:90(11):1364-8 [PubMed PMID: 15486149]
Kabukcu M, Demircioglu F, Yanik E, Basarici I, Ersel F. Pericardial tamponade and large pericardial effusions: causal factors and efficacy of percutaneous catheter drainage in 50 patients. Texas Heart Institute journal. 2004:31(4):398-403 [PubMed PMID: 15745292]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence